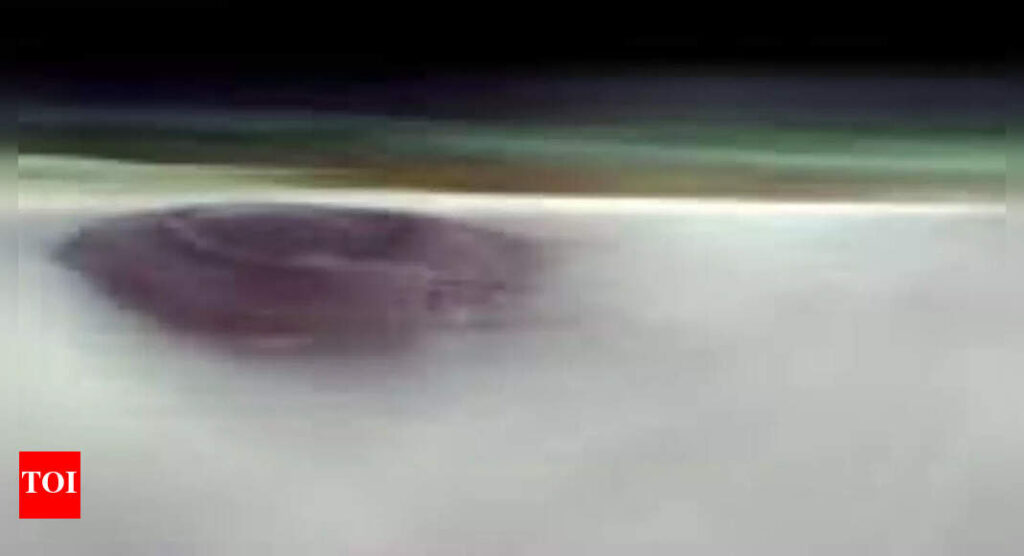
NASA has captured a breathtaking image of Arsia Mons, one of Mars’ most massive volcanoes, towering nearly twice the height of any mountain on Earth. Captured at dawn by the 2001 Mars Odyssey orbiter, the photograph shows the volcano piercing through a layer of early morning haze, offering a surreal glimpse into the Martian horizon. Beyond its visual beauty, the image provides crucial scientific insights into Mars’ volcanic past and atmospheric behaviour. Located in the Tharsis region, Arsia Mons’ immense scale and persistent cloud cover make it a key subject for studying the Red Planet’s evolving climate and geology.
NASA’s Mars Odyssey captures stunning image of Arsia Mons volcano
NASA’s Mars Odyssey spacecraft captured the breathtaking photo of Arsia Mons using its Thermal Emission Imaging System (THEMIS). The image is of the volcano above a green-colored haze of clouds passing over the Martian horizon at sunrise. The summit caldera of Arsia Mons is 120 kilometers wide, and it is larger than most volcanoes on Earth.For comparison, Arsia Mons is approximately 20 kilometers high, roughly twice as tall as Mauna Loa in Hawaii, the tallest volcano on Earth and roughly 9 kilometers higher than the sea bed. “We were hoping to grab Arsia Mons rising above morning clouds—and it surely didn’t disappoint,” joined Arizona State University’s THEMIS operations lead Jonathon Hill.
NASA studies Martian clouds and seasons using Arsia Mons observations
Arsia Mons is located in the Tharsis province of volcanoes on Mars, which has three colossal volcanoes. The southernmost and typically cloudiest of the three is Arsia Mons. Its thick cloud cover is most common at Mars’ aphelion—the time when Mars is farthest from the Sun. The clouds play an important role in Martian climate observation and phenomena like the planet’s notorious dust storms.To record such seldom-observed horizon vistas, the Mars Odyssey orbiter performs a special 90-degree rotation maneuver so that its primarily ground-pointing camera may take pictures of the planet’s atmospheric horizon. This special technique enables scientists to track dust and water-ice clouds and analyze their seasonal trends.Planetary scientist Michael D. Smith at NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center commented, “The horizon images exhibit large seasonal variations. These measurements are teaching us new things about how Mars’ atmosphere varies with time.”
Why Arsia Mons volcano image matters
In addition to its photographic attractiveness, the image of the Arsia Mons contains rich scientific information about Mars’ geology and climate. Scientists gain a better understanding of predicting weather, dust storm formation, and the workings of larger-scale planetary phenomena by examining such volcanic formations and their interaction with the atmosphere.This image is particularly important as the space agencies of the world hasten plans to send man to Mars and increase robotic missions to the Red Planet. Such images pave the way for more safe and informed voyages to the Red Planet and take man one step closer to discovering its mysteries.Also Read | June 2025 stargazing: Witness the rare glimpse of the Milky Way’s glowing core, planetary alignments and more this month; here’s how










More Stories
Earth shook every 90 seconds for 9 days in 2023; scientists finally reveal the shocking reason |
Sellafield could leak radioactive water until 2050s, MPs warn
‘Doomsday’ oarfish surfaces in Tasmania’s wild west coast